Zhejiang park boasts unique ecosystem


Rich biodiversity
The area is home to 61 species of rare and endangered plants, 14 of which are native to China, as well as a diverse avian community, and accounts for over half the bird species found in Zhejiang.
China's forestry authorities say that an ecosystem of this scale is unique in the world, according to Fu Bojie, an academician at the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
"It is of great value to environmental protection and scientific research worldwide," Fu said.
Qianjiangyuan is also home to rare and endangered animals, including natives such as the black muntjac, an animal that Wei Fuwen, another CAS academician, said was comparable to the giant panda. Worldwide, about 10 percent of black muntjacs, which belong to the deer family, live in Qianjiangyuan.
A few hundred kilometers to the south lies the Baishanzu area of the park. Situated in Qingyuan county, Lishui city, it is named after one of the highest mountains in the area and covers 505 sq km. Some 1,860 meters in height, Baishanzu literally means the "ancestor of hundreds of mountains", which speaks of its significance.
Much like Qianjiangyuan, Baishanzu is also a natural habitat for rare and endangered species. Visitors can see the world's rarest conifer, the Baishanzu fir, or Abies beshanzuensis. Currently, the reserve is home to just three of the trees, which have been classified as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
In addition, 2,102 species of vascular plants, 416 vertebrates and 632 macrofungi have been identified in the Baishanzu area.
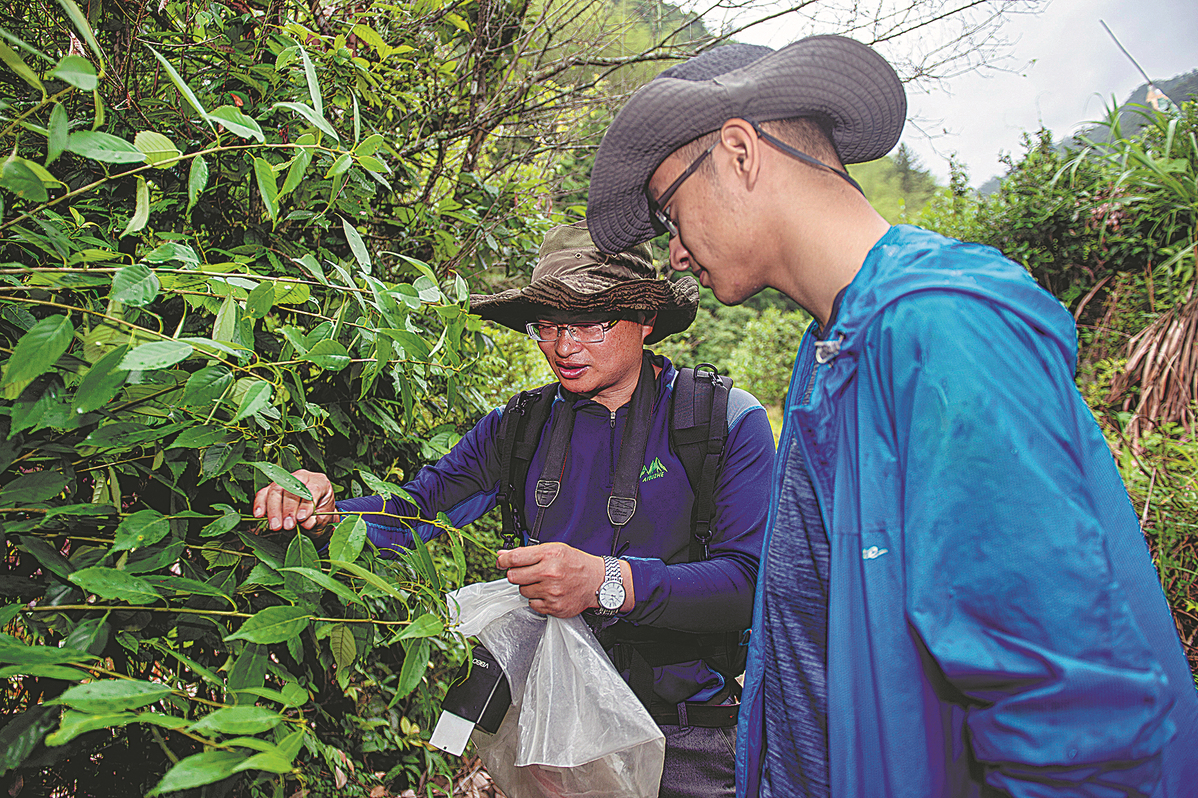
The rich ecosystem and biodiversity of the national park have become a focus of research for both Chinese and foreign scientists, who have set up biodiversity monitoring platforms, research stations and climate change centers. In June, a new species of frog was discovered in Baishanzu during a biodiversity survey, and has been aptly named Megophrys baishanzuensis.
The research programs also support China's ongoing efforts to protect wild flora and fauna and their habitats in recent years. In late May 2019, scientists from Zhejiang University successfully returned three artificially-cultured Baishanzu fir seedlings to their natural habitat, just a year after they had cultivated the world's first Baishanzu fir seedlings using embryo technology. More is being done to expand the naturally grown population of these living fossils, and it is hoped the species will eventually be removed from the critically endangered list.