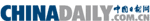Buddha's gaze into eternity
Son's devotion shines down for centuries in a grotto that still fascinates, Zhao Xu and Ma Jingna report.


The Buddhist deities depicted here have round faces, thick lips, deep-set eyes and high-bridged noses. Their physiques are strong and well-defined, yet their poses are fluid and graceful, almost dance-like. Draped in delicate, flowing garments, they embody the elegance and allure of iconic Indian beauty, she says.
"The Tianti Mountain Grottoes bear witness to Indian Buddhist art in its earliest, most unassimilated form upon reaching China," she adds.
Within the next century, local adaptation brought classical Chinese aesthetics, along with influences from Confucianism and Taoism. Figures became more slender, their garments more spacious, with flowing belts that added a sense of elegance and refinement.
In 439, the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) unified northern China by ending the control of the Hexi area by Northern Liang. Following their victory, the Northern Wei rulers relocated nearly all prominent families and artisans to their capital in modern-day Datong city, Shanxi province, about 1,100 km northeast of Wuwei. These craftsmen later contributed to the creation and decoration of Buddhist grottoes in the heartland of China, spreading what one prominent Chinese archaeologist dubbed "the Liangzhou Model".
It's worth noting that in world art history, this style of human statue-making, characterized with natural proportions, expressive faces and the contrapposto pose, are recognized as part of the tradition of Gandhara Art. Flourishing between the 1st century BC and 5th century in present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, this style, which blended Greco-Roman realism with Indian traditions, emerged through Alexander the Great's invasion in the 4th century BC and the subsequent Greek rule in parts of India. It later received significant patronage under the Kushan Empire (1st-3rd centuries), whose founders are Rouzhi people who once occupied part of the Hexi Corridor and with whom Emperor Wudi of China's Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220) had tried unsuccessfully to form an alliance against the Xiongnu raiders.
Keeping this in mind, it's equally intriguing to note that Juqu, the man behind the Tianti Mountain Grottoes, likely had both Rouzhi and Xiongnu blood, a fact that speaks as much about the complicated history of the Hexi Corridor as about the broader formation of Chinese civilization.
In fact, many scholars suggest that Juqu's efforts at Tianti Mountain were ultimately politically motivated. In a place like the Hexi Corridor, where consolidating power had been no easier than stabilizing sand, Buddhism served as a key unifying force that even a fierce ruler like Juqu would have needed to rely on to win hearts and minds.
And in that, Juqu, if he had lived a long life, would have found a like-minded person in a Mongol prince named Borjigin Godan (Kuoduan in Chinese), grandson to Genghis Khan and son to Ogedei Khan.
In 1247, Godan met with Sakya Pandita (commonly known as Sapan) in Wuwei. A revered Tibetan spiritual leader and Buddhist scholar, Sapan had spent two years traveling with his two young nephews, including 9-year-old Chogyal Phagpa. This meeting paved the way for the inclusion of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau into the rule of Yuan Dynasty, founded by Kublai Khan, another grandson of Genghis Khan, in 1271. One year before, Kublai made Phagpa, then 35, his imperial preceptor.
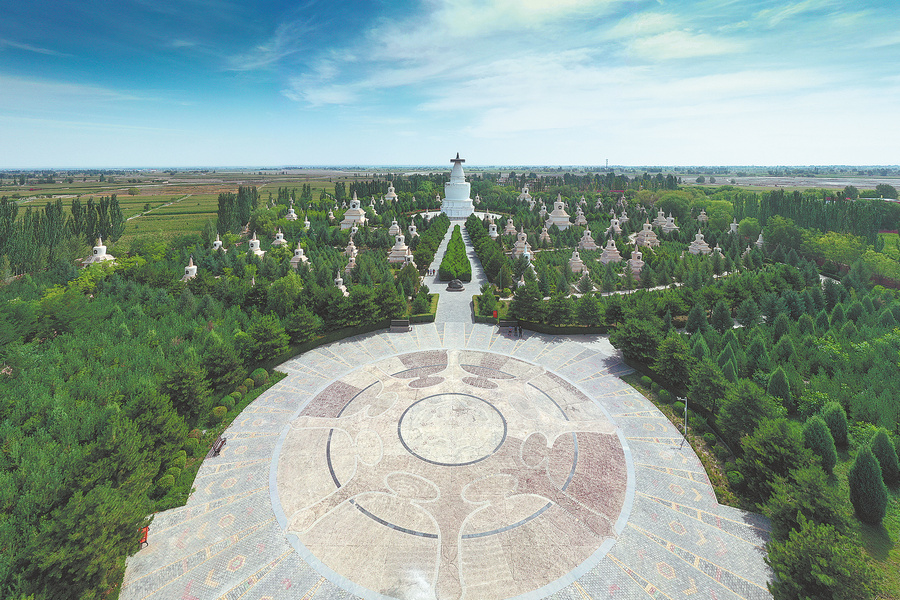

Today, the place to reflect on that history is Wuwei's Baita (White Tower) Temple, where Phagpa lived until his passing in 1251 at the age of 69. His cremated remains, known as sarira in Buddhism, were buried there within the base of a memorial tower built in his honor by Godan, who had adopted Tibetan Buddhism as his belief.