Economics
(Wikipedia)Updated: 2006-09-30 15:29
Economics is a social science seeking to analyze and describe the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. That is, economics studies how individuals and societies seek to satisfy needs and wants. Alfred Marshall informally described economics as "the study of man in the ordinary business of life" in the late 19th century; the vast number of topics to which the methods of economic theory have been applied suggests to some that economics is simply "that which economists do."
The word "economics" is from the Greek words 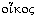 [oikos], meaning "family, household, estate," and
[oikos], meaning "family, household, estate," and 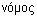 [nomos], or "custom, law," and hence means
"household management" or "management of the state." An economist is a person
using economic concepts and data in the course of employment, or someone who has
earned a university degree in the subject.
[nomos], or "custom, law," and hence means
"household management" or "management of the state." An economist is a person
using economic concepts and data in the course of employment, or someone who has
earned a university degree in the subject.
Economics has two broad branches: microeconomics, where the unit of analysis is the individual agent, such as a household or firm, and macroeconomics, where the unit of analysis is an economy as a whole. Another division of the subject distinguishes positive economics, which seeks to predict and explain economic phenomena, from normative economics, which orders choices and actions by some criterion; such orderings necessarily involve subjective value judgments.
Economic reasoning has in recent decades been increasingly applied to social situations where there is no monetary consideration, such as politics, law, psychology, history, religion, marriage and family life, and other social interactions.
The approach to economics that is dominant today is usually referred to as mainstream economics. The more specific definition this approach implies was accurately captured by Lionel Robbins in 1932: "the science which studies human behaviour as a relation between scarce means having alternative uses." Scarcity means that available resources are insufficient to satisfy all wants and needs; absent scarcity and alternative uses of available resources, there is no economic problem. Heterodox economics, including institutional economics, Marxist economics, socialism, and green economics, sometimes make other grounding assumptions, such as that economics primarily deals with the exchange of value, and that labour (human effort) is the source of all value.
| 1 | 2 |  |
(For more biz stories, please visit Industry Updates)