Despite the rapid development of its intermediate and capital goods sectors, China nonetheless continued to ramp up its imports of such products from developed economies. While still relatively small, developed economies' exposure to China's domestic market has swelled, with their exports to China as a share of GDP more than doubling from a decade earlier. The EU dominates China's import markets for chemicals, machinery and transport equipment.
Since 2003, EU and Korea have made the greatest inroads into China's chemicals import market, as the share of Japan, the US and Taiwan in the mainland’s chemicals imports declined.
The EU's dominance in China's machinery import market, meanwhile, has a relatively longer track record. Japan, however, has seen its share in this market diminish in the past decade, especially since 2011, in part due to the severe production disruptions triggered by a tragic earthquake and tsunami, and in part due to loss of market share to Korea. Korea's gain in market share in the electrical machinery and equipment market in China is especially notable. Where transport and vehicles are concerned, Europe also dominates China's import market, with its prominent rise in recent years again seemingly obtained at Japan's expense. That said, the latest data suggests that perhaps both the US and Japan are making a comeback in this sector.
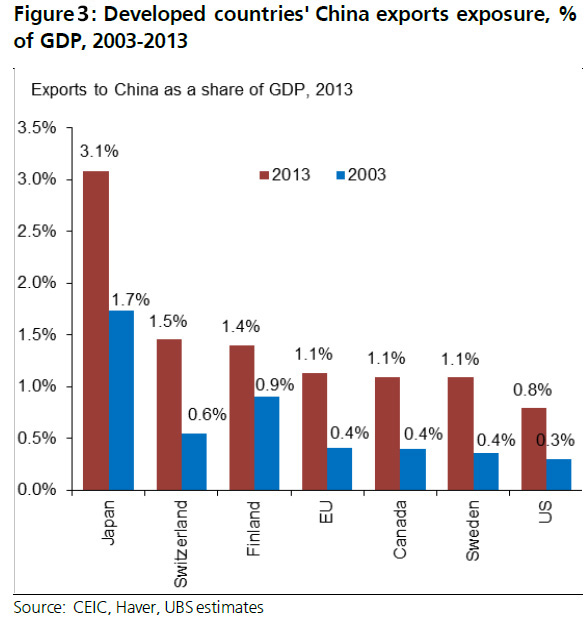
The robust growth of EU exports to China over the past decade implies increased vulnerabilities of some European economies to a significant China slowdown. Our global industrial analysts estimate that for the decade to 2013, China made an average contribution of 12 percent to the European industrial sector's revenues, but substantially more when the indirect uplift that China's growth has had on demand markets elsewhere is included – up to 30-40 percent of total profit growth. Machinery exports to China as a share of exporters' GDP (including exports that went via other countries before arriving in China) quadruped for Germany, tripled for France, rose by 2.5 times for Sweden, and doubled for Japan between 2000 and 2009.
A significant slowdown in China's property construction and investment growth will not only lessen China's appetite for foreign industrial imports, but could also push for higher Chinese exports to the global market. This, in turn, underpins their expectations for the European industrial sector's long-term growth rate to fall short of GDP in the years ahead, as has already started to happen in the power generation equipment and truck sectors.
Outside of commodity exporters, Korea, Taiwan and other regional economies have the highest exposure to the mainland. Asia ex-Japan's exports to the mainland have been boosted both by the mainland's own rapid growth and by a deepening of the regional supply chain, the latter especially applicable to Korea and Taiwan, and the electronics sector. The last feature also implies that the importance of China as a final exports destination is often overstated by headline data for China-bound exports. If we take into account the share of imports used as inputs for processing exports, the "true" exposure of Asian economies like Korea, Taiwan, Malaysia and Thailand becomes smaller.
Since the onset of the global financial crisis, the role of processing exports in overall Chinese exports has declined, partly due to weaker developed market demand, and partly because of China's eroding competitiveness in certain labor intensive sectors. This change in China's processing trade is also reflected in China's shifting trade balance with its major trading partners over the past decade. Before 2005, China's widening trade surplus with the US and Europe was mirrored by its widening trade deficit with non-Japan Asia. Since the GFC, the decline in China's surplus with the US and Europe has also been mirrored by the drop in its deficit with non-Japan Asia.
The article is co-authored with other UBS economists Donna Kwok, Harrison Hu and Ning Zhang. The views do not necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
