
|
CHINA> Focus
 |
|
Peking Opera troupes take bold steps to be profitable
By Liu Jie and Hou Qingyang (China Daily)
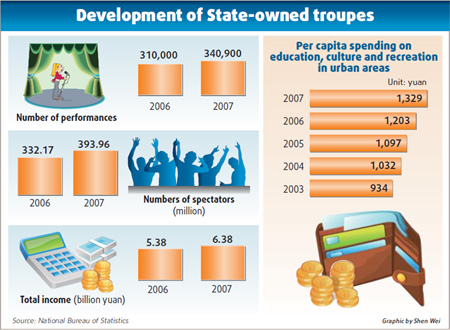
Updated: 2009-06-22 10:49 Market-oriented "This kind of project-oriented cooperation would have been unimaginable before the market-oriented reform process," said Hu Huiling, a Shanghai Jiaotong University professor who specializes in China's cultural industry. "Now (after reform) we have got the right to design products independently; but since we cannot get fiscal support anymore, we are forced to make every effort to cater to the audience and become competitive in terms of products, services and business operations," Zhang Yu, the general manager of China Arts and Entertainment Group, said during a recent interview to CCTV. Wang Hongbo said raising funds from the market meant that the company was free to devise a long-term development strategy instead of coping with short-term issues like balancing its meager budget. To all intents and purposes, the move out of the government's shadow seems to be paying off. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, from 2006 to 2007, the peak period when State-owned troupes around China started to embrace market-oriented reforms, the number of performances went up 9.97 percent, from 310,000 times to 340,900 times. The total revenue of these State-owned troupes also surged 18.72 percent, from 5.38 billion yuan to 6.38 billion yuan. Data from China's Ministry of Culture showed that in 2004 there were 90 Peking Opera troupes, and their combined income was less than 45 million yuan. Though they were then massively subsidized by the state, audience numbers had started dwindling. But the trend has reversed post reform and many troupes have started to make money. The China National Peking Opera Company gets 2 million yuan from the operators of the Mei Lanfang Grand Theater for 100 performances each year from 2008 to 2012. Retaining good artistes requires market-oriented pay system "I have never seen the Peking Opera in so magnificent a building," said Wang Jianmin, a 58-year-old Beijinger and loyal Peking opera fan, whose son gave him tickets for a performance during this year's Spring Festival. "But the ticket rates are expensive; I prefer to watch it at Changheyuan where each ticket costs only 50 yuan." The more pressing concern, however, is how to retain good artistes, and that is an issue the troupes should ponder seriously, professor Hu said. "In the past, the salary was fixed under a system formulated by the government; the market mechanism has made the payment system disparate, resulting in competition within the industry," Hu said. "But management of actors, who are usually emotional people, is not easy. In addition to money, more chances to perform, encouragement and open communication should be fostered," Hu said. Wang Ying, the general manager of China Children's Arts Troupe, said her company has adopted a flexible salary system in line with performance metrics and a top artiste at her company can earn more than 10,000 yuan per month, compared to a monthly income of 2,000 to 3,000 yuan under the State-subsidy regime. The annual salary and insurance expenses for its 100-plus employees surged from 2 million yuan in 2003, a year prior to the market reform, to more than 7.5 million yuan last year. From a cultural unit supported by the central government, the troupe turned into a joint venture company in late 2004. Its five shareholders - the Beijing Youth Daily, Cultural Facility Operation and Management Center under the Beijing Ministry of Culture, the TV Industry Development Center of Beijing Television Station, High School Property Development Co Ltd of Beijing Education Commission, and the Beijing Cultural Development Center - have invested 40 million yuan cumulatively in the venture. The China Children's Art Troupe gave 303 performances in 2006, generating 55 million yuan in revenue. It did 398 shows in 2007 and 666 in 2008, with income touching 62.64 million yuan and 75.60 million yuan, respectively, for both years. The troupe last year performed the children's fictional play Fuwa, based on the mascots of the Beijing Olympic Games. The play depicted how the five fuwas united to overcome difficulties and challenges and make the world peaceful and harmonious. Later, the company built several small-sized Fuwa amusement parks catering to children in Beijing, China's capital city. The revenue from this business alone has the potential to make up one-fourth of its income going forward, insiders said.
|
主站蜘蛛池模板: 顺平县| 宁都县| 贵州省| 绥中县| 西乌| 德安县| 突泉县| 博罗县| 景宁| 繁昌县| 邵阳县| 陈巴尔虎旗| 金寨县| 济宁市| 荣成市| 个旧市| 厦门市| 洪洞县| 柏乡县| 绥棱县| 金昌市| 稻城县| 六盘水市| 犍为县| 怀来县| 营山县| 从江县| 饶平县| 镇巴县| 河池市| 东兴市| 日土县| 大埔区| 五华县| 新蔡县| 丹江口市| 阜康市| 丹凤县| 新巴尔虎左旗| 开原市| 桂林市| 彝良县| 襄汾县| 天津市| 辉县市| 玉环县| 望城县| 乳山市| 九龙县| 三明市| 南乐县| 荃湾区| 保亭| 榆中县| 宁都县| 大理市| 盘山县| 长岛县| 芷江| 清涧县| 新建县| 公安县| 安福县| 银川市| 迭部县| 临夏县| 丹寨县| 兴业县| 宁武县| 萍乡市| 沿河| 博罗县| 房山区| 田东县| 木里| 余姚市| 永仁县| 苏尼特右旗| 平潭县| 昌宁县| 扶绥县| 信阳市|