Preserving China's industrial heritage
 |
|
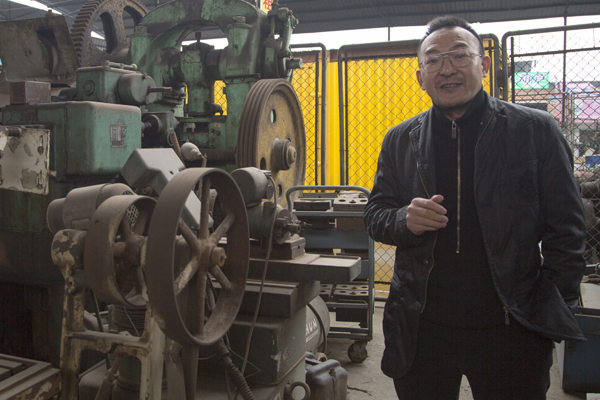
Tang Shigang poses with part of his collection of antique machine tools in Chongqing. [Photo provided to China Daily] |
Tang Shigang is a painter with a passion for antique machinery.
The 53-year-old has spent more than two decades collecting 36 large machine tools dating from the 19th century through to the 1930s.
Most were imported from Germany, the United States, Switzerland and the former Soviet Union, although a few were made by China's first arsenals, built during the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911).
"These machines witnessed the country's earliest period of industrialization and the development of new technology," Tang said. "Unfortunately, most of them were destroyed and are now gone forever."
China's first arsenals were established as part of the Qing government's Self-Strengthening Movement, which came in the wake of a series of military defeats and concessions to foreign powers.
Equipped with modern machinery and advanced technology imported from abroad, these factories played an important role during the War of Resistance Against Japanese Aggression (1931-45), with the arsenals in Chongqing alone producing almost two-thirds of the munitions used.
Tang, who graduated from Chongqing's prestigious Sichuan Fine Arts Institute in 1989, first worked as an arts teacher at Neijiang Normal University in Sichuan province.
He quit his job in 1995, choosing instead to trade in mechanical and electrical equipment, but his passion for collecting machine tools was not ignited until two years later, when he came across a rusted milling machine that had been imported from Germany in the 1880s.
It belonged to a scrap dealer who was planning to melt it down. "In the eyes of an artist, this old machine is exceptional," Tang said.
"It would have been a huge pity if it were melted down."
Once the seller realized that Tang was interested, he immediately raised the price to 9,000 yuan ($1,300) - a sum that the artist could only afford by borrowing from friends and family.
Little did Tang know then, but this first purchase would set him down a path toward collecting several million yuan's worth of antique machinery over the years.
He purchased much of it at public auctions in the 1990s, as local State-owned factories began to upgrade their technology.
"I just wanted to save as many of these precious items as I could," he said.
Few others were interested in saving the historical equipment, preferring instead to dismantle it and sell it for scrap.
Over time, this led to fewer and fewer examples of antique machinery coming to market - the last time Tang found a new addition for his collection was in 2010.
And his efforts have been further frustrated because he was not always able to acquire the items that he found.
In the 1990s, he discovered a made-in-China shaper at a State-owned arsenal that had been donated by the Soong sisters - three women who, along with their husbands Sun Yat-sen, Chiang Kai-shek and Kung Hsiang-Hsi, were among China's most significant political figures of the early 20th century.
The machine could not be used any longer so Tang asked the factory to sell it to him, but his request was refused.
"That machine just disappeared," he said. "My heart was broken too."
Tang has devoted himself to researching the history of the machine-tool industry and has become an expert at identifying an item's age and history just from seeing its designs.
He now plans to open a museum in Chongqing to display his collection and raise awareness of China's industrial heritage.
The rusted machines in Tang's possession are not just historical relics, either.
"Eighty percent of them are still operable if properly maintained," he said.