 |
|
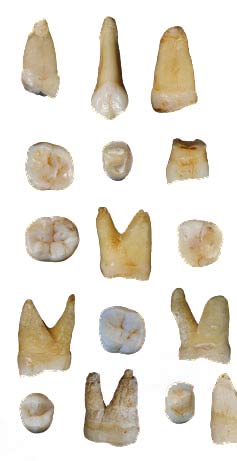
Some of the 47 human teeth discovered in a cave in Hunan province. Provided to China Daily |
The discovery of 47 human teeth in a cave in Hunan province by Chinese scientists has unearthed new evidence that the earliest modern humans lived in East Asia.
The teeth and a number of animal fossils were excavated from Fuyan Cave in Daoxian county.
After geological dating tests and analysis, the scientists determined that the teeth belonged to Homo sapiens, the species of modern humans that lived between 80,000 and 120,000 years ago.
The discovery of the teeth, made between 2011 and 2013, has just been reported in the online version of the scientific journal Nature.
Nick Campbell, the journal's executive editor, said, "The human teeth from China ... open up a new window on an area we had little information on before.
"These fossils ... are approximately double or more the age of any previous well dated, well preserved human fossils from southern Asia."
The first appearance of humans in the eastern Mediterranean and East Asia has remained a mystery due to lack of fossil evidence.
Human fossils found earlier in Beijing's Tianyuan Cave, Huanglong Cave in Hubei province and Zhiren Cave in the Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region narrowed this down to between 11,000 and 40,000 years ago, but none of these species evolved fully into modern humans.
Liu Wu from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and lead author of the paper in Nature, said, "This is a milestone discovery because the species we found in the Fuyuan Cave is from well developed modern humans, almost identical to living humans.
"This means that we were present in southern China 30,000 to 70,000 years earlier than in the eastern Mediterranean and Europe."
Campbell, from Nature, said, "The findings really do substantially change our understanding of how modern humans established themselves in Asia.
"The findings may have some intriguing implications for the ever-evolving story of how modern humans replaced Neanderthals."
Neanderthals were closely related to modern humans and lived between 24,000 and 130,000 years ago.
They were smaller than modern humans and had low, flat elongated skulls.
Maria Martinon-Torres from University College London, a co-author of the paper, said, "Now we know that modern humans were present in southern China as early as 80,000 years ago, but there is no evidence that our species entered Europe before 45,000 years ago, when Neanderthals were already extinct."
Robin Dennell from the Department of Archaeology at the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom, said of the teeth discovery, "More revelations about our species' history can surely be expected from southern China."
chengyingqi@chinadaily.com.cn??
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
