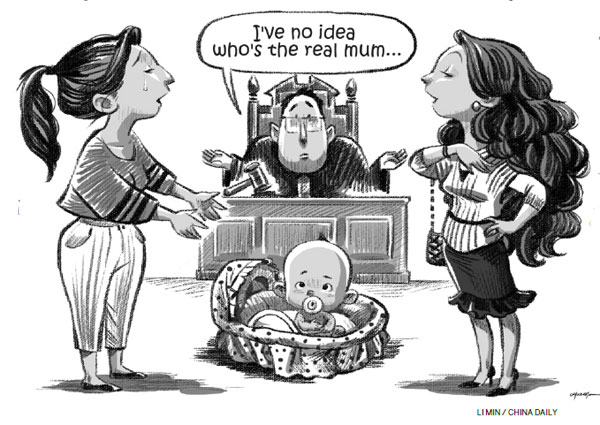
Surrogacy not just a reproductive rights issue
Reproductive rights include the right to have or not to have children. Reproductive rights are protected by national laws and national legal restrictions, which is actually a legal issue.
The comprehensive two-child policy that came into effect on Jan 1 also allows couples in their late 30s and 40s to have a second child. But some these eligible but relatively aged couples may have to turn to special reproductive technology to realize their dream. So whether China will allow surrogacy has become a vital question.
Citizens in exercising reproductive rights must be "consistent with conditions determined by the law and regulations". Chinese people using reproductive technology to have children must comply with the relevant provision of the People's Republic of China Population and Family Planning Law. Plus, the regulations "prohibit the use of ultrasound technology and other technical means to identify the gender of fetuses for non-medical needs and prohibit sex selection for non-medical needs of pregnancy termination". In other words, China is implementing a natural fertility law, which does not encourage human or technology intervention in reproduction.
Although China has approved in vitro fertilization, it has always been cautious on non-labor fertility issues. Therefore, some media reports' assumption that China does not prohibit surrogacy is not true.
The fact is China does not encourage or promote surrogacy. First, China's regulations on medical practitioners clearly says that qualified medical practitioners should not engage in such activities. If they are found overtly or covertly performing surrogacy surgery, their certificates could be revoked.
Second, China's health and family planning administration department issued a series of regulations aimed at eradicating illegal trading activities including those related to surrogacy. And if medical institutions help carry out such surgeries, their business licenses could be can celled.
Third, China's legal system does not protect surrogate motherhood. For women who engage in illegal reproductive activities, their personal rights are not protected by any law.
All in all, the revised PRC Population and Family Planning Law does not have any compromising content on surrogacy.
Although China has allowed some medical institutions to conduct research in In vitro fertilization, the administrative organizations strictly prohibit surrogacy for commercial purposes.
Surrogacy is not just an issue of reproductive rights; it also involves a series of ethical issues. As some cases show, the legal dispute over surrogacy is very complex. Whether or not children are born to biological mothers, they all require proper care and protection. How surrogate mothers should be protected by the law, however, needs to be determined by serious in-depth studies and the judiciary.
From the child-protection point of view, China should encourage surrogacy, for infertile couples. But couples who need complementary fertility assistance to have children can seek the help of national statutory medical institutions. In other words, China has not completely banned assisted reproductive technology through approved medical institutions, but to have access to it couples have to pass through strict procedures. The technology can help legally married couples have children.
In vitro fertilization is not new in China, but it involves complex relationships and laws. Despite this, the revised law as the basic family planning law of China for special reproductive technology does not have detailed provisions.
But with reproductive technology continuing to improve, China is expected to develop appropriate technology and ethical norms. And once that is done, assisted reproductive technology will provide Chinese couples with more reliable help.
The author is a professor of law at Zhongnan University of Economics and Law.