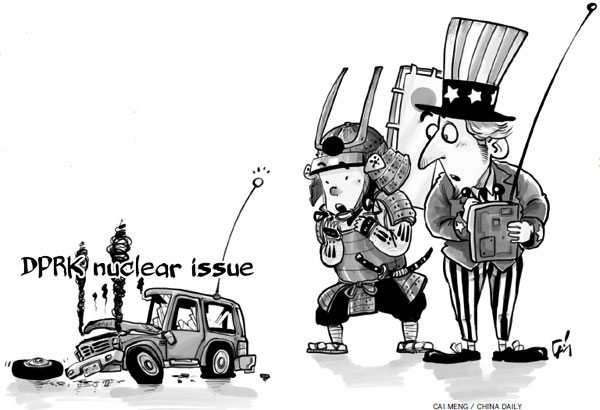
G7 cannot speak for all on DPRK nuclear issue
The 2016 G7 Summit, which will be held in Ise-Shima, Japan, on Thursday and Friday, comes at a time of rising strategic tensions in Asia.
According to the agenda, social issues and global growth are to be discussed, as are hot security affairs, including the Democratic People's Republic of Korea's nuclear issue, which Japan would like to see reflected in a G7 joint statement.
Pyongyang's fourth nuclear test in January, in particular, has fueled global concerns over possible nuclear proliferation on the Korean Peninsula. However, for some G7 members, such as the United States and Japan, playing up the DPRK's nuclear threat is also part of their strategic intentions.
Japan, which is hosting the two-day talks, is keen to win an endorsement for its position as a "normal state" in the international community, and is playing up the threat of the DPRK having nuclear weapons. The US, too, is highlighting the dangers of the DPRK's nuclear ambitions to justify its rebalancing to the Asia-Pacific.
Nevertheless, the G7 summit that involves Canada, France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom, as well as the US and Japan, is still not an appropriate platform for discussing the DPRK nuclear issue, which concerns the international society as a whole. That explains why it was the UN Security Council that passed the four resolutions against Pyongyang's nuclear tests.
Admittedly, the group plays a certain role in global governance, but it was founded over four decades ago to boost economic cooperation in the West, thus it does not represent all parties concerned in the nuclear issue.
Only two G7 members - the US and Japan - are part of the Six-Party Talks aimed at denuclearizing the peninsula, which have been indefinitely stalled since 2008. The other parties are China, the DPRK, the Republic of Korea and Russia.
Any consensus reached by G7 leaders on the DPRK nuclear issue, if there is one, will hardly be convincing without the other participants in the Six-Party Talks, and may further complicate the situation.
What the all parties should do is to fully implement Resolution 2270 passed by the UN Security Council on March 2, which includes economic sanctions against Pyongyang, as well as measures aimed at bringing it back to the negotiation table.
Should the G7 members propose to independently take additional measures, which is likely, the DPRK may seek to enhance its nuclear advocacy "in response to the security threats from the West", especially the US.
The rising tensions on the peninsula are, of course, a result of Pyongyang's and Washington's flawed strategies as well as the decades-long Cold War situation. But it does not mean the G7 joint statement cannot touch upon nuclear non-proliferation, given Pyongyang's latest reiteration of its nuclear ambitions.
After the DPRK's top leader Kim Jong-un assumed power less than five years ago, the country has already conducted two nuclear tests. The 7th Congress held by the ruling Workers' Party of Korea earlier this month, the first major conference of the party in 36 years, also indicated that Pyongyang will keep pursuing the development of nuclear technologies as a "responsible nuclear power".
In this light, mentioning non-proliferation in the G7 joint statement would instill in Pyongyang the fact that the international community will not allow the existence of a large nuclear arsenal on the Korean Peninsula.
On its part, the DPRK should drop the wishful thinking that diplomatic maneuvers and consistent nuclear advocacy will keep negotiations at bay.
It is important that the G7 nations refrain from going too far and exacerbating the situation.
The author is an associate researcher at the National Institute of International Strategy of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences.