Elegant toilet culture can boost tourism
Chinese people now enjoy quality lifestyles in almost every aspect. Yet there's one thing that's too often missing, and it hurts tourism efforts
On May 19, China celebrated its sixth National Tourism Day. China's domestic tourism market has boomed in the past decade, with 10 percent annual growth on average and spending that is expected to reach around $890 billion by 2020.
However, the bottleneck in China's domestic tourism market is now none other than its toilets, which have been called inadequate, dirty and chaotic. As Li Jinzao, head of the China National Tourism Administration, has pointed out, a dirty toilet destroys the efforts of all kinds of tourist resort promotions and their negative impact is hard to erase.
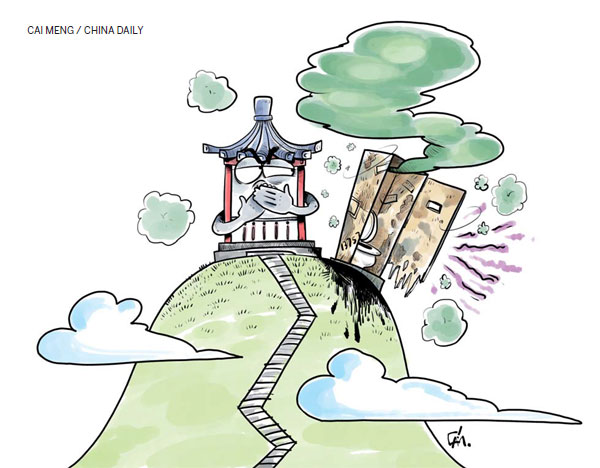

That was why the authority launched a nationwide, three-year "tourism toilet revolution" in January 2015, with the goal of building and reconstructing 57,000 public toilets by the end of 2017. Only last year, more than 20,000 new toilets were built.
Actually, Beijing's 2008 Olympic Games was the beginning of China's toilet revolution. In an effort to ensure their success, the Chinese government invested billions of yuan into building 4,000 new public toilet facilities to world-class standards. To showcase the great progress that was made, Beijing hosted the World Toilet Summit in 2004, with the help of the World Toilet Organization.
There is no doubt the Chinese government has the capability to deliver any ambitious infrastructure commitment quickly. But it is the software that is critical to the success of the toilet revolution. China's toilets are generally unevenly scattered, poorly managed and low in quality.
That could be remedied by following the ABC rule, namely architecture, behavior and cleaning.
First of all, public toilets have to be user-friendly to a wide variety of people of both genders, from mothers with babies to children and adults, as well as the elderly and disabled. Architects and the facility owners need to be "toilet trained" so that they understand how to design for different types of buildings and the needs of different demographics.
However, behavior is the most critical part for success. It includes environmental conditioning inside the toilet that guides the user's behavior as well as the awareness of behavioral norms of society at large. To promote public education of toilet usage, both rational and aspirational approaches are needed. Past experience shows that rather than lecturing posters, motivating aspirations of personal elegance often proves most successful. When a toilet respects the users, the chances of reciprocal respect from the user are also higher.
Clean toilets also require the professionalization of cleaners, facility managers, and owners. The right training, equipment and supplies are critical success factors. In fact, many public toilets in China have been constructed according to high standards, but as the management is not up to the same standards, they become dirty and fall into disrepair quickly.
The ancient Chinese had a culture of recycling excreta into fertilizers and this practice created plenty of toilet designs that facilitated the manual collection of excreta, especially in rural areas even today. Since these designs were not focused on the enjoyment and privacy of the individuals, an elegant toilet culture did not develop in many parts of China.
Now, with the past 30 years of rapid economic growth, Chinese people enjoy quality lifestyles in almost every aspect. Yet an elegant toilet culture is still missing. It has caused major anomalies and incurred many complaints both inside and outside China. Therefore, promoting a better toilet culture will not only boost more inbound tourists, it will also be welcomed by the host countries receiving outbound Chinese tourists.
Jack Sim is founder of the World Toilet Organization and visiting fellow at the Institute of Water Policy of the Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy at the National University of Singapore. Sun Xi is an independent commentary writer based in Singapore and alumnus of the Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy. The views do not necessarily reflect those of China Daily.