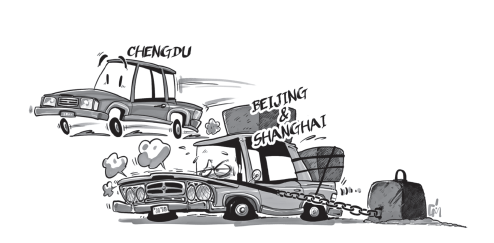
Chengdu good example for managing car-hailing
 |
|
Cai Meng/China Daily |
Of the more than a dozen Chinese cities that have recently released their draft plans on management of car-hailing services, Chengdu, capital city of Southwest China's Sichuan province, is arguably the most tolerant.
In general, the tone of its draft rules is softer and more considerate. Unlike Beijing which requires ride-sharing drivers to possess a local household registration, and their vehicles to have engine displacements of at least 2.0L or 1.8T and a wheelbase longer than 2.65 meters, Chengdu demands none of that. Rather, it has made clear its confidence in the sharing economy and the market.
To encourage citizens to choose greener, safer and more efficient transport, Chengdu has set specific rules ranging from drivers' responsibilities and information security to passengers' right to supervise and make complaints, and it has elaborated on each of them.
In particular, its pledge to compensate passengers if their complaints are well-founded but remain unanswered by the drivers, sets a good example for the protecting of residents' legal interests that should be learned by other Internet Plus business models. In comparison, other cities have been inclined to take a different approach-setting higher thresholds for drivers to stay in the car-hailing business-in an attempt to protect passengers.
However, keeping a tighter rein on ride-sharing platforms such as Didi Chuxing and their drivers is not necessarily in line with people's needs and demands and may cast a shadow over the innovation-driven economy. The Beijing government, for example, said it would exercise its pricing right "if need be". The government in Chengdu, on the other hand, has promised to let the market decide how much passengers should pay for their rides.
Relinquishing the government guided-price system, in fact, is unlikely to cause irrational pricing in the ride-sharing market. When an oversupply of vehicles occurs, more drivers will choose to quit as their earnings will wane as passengers opt for the cheapest ride pushing down prices and thus drivers' incomes. Likewise, an undersupply could lead to a rise in fares that would attract more drivers to get involved. The market always better judges how many taxis are required than transportation authorities.
But the clashes are not just between these visible and invisible hands, but also between traditional taxis and emerging ride-sharing cars. Chengdu government's solution is to break the boundaries that separate them. According to its latest draft rules, qualified taxi drivers are allowed to use car-hailing platforms without giving up their job with a traditional taxi company or using another car.
On the one hand, they have the freedom to choose the way of doing business on the basis of market demand, and can work for multiple platforms at the lowest cost. On the other hand, the integration between taxi industry and car-hailing services is a boon to the former's long-sought reform. Beijing and Shanghai are right to buy some time for an overhaul in the management of taxis, but this cannot be done at the cost of the ride-sharing business. They are better dealt with together than separately.
On the qualifications for car-hailing drivers and vehicles, Chengdu's plan also makes more sense. It not only welcomes new energy vehicles to the ride-sharing business, but also has less strict requirements for engine displacement (1.6L and 1.4T or above). Besides, non-local drivers with a local residence permit can also work for car-hailing platforms.
Beijing's draft regulations would exclude traditional taxis and high-end vehicles, as well as non-locals, from the ride-sharing business. The household registration restriction is controversial, unnecessary, even a bit discriminatory, and may be deemed invalid because it contradicts with the Administrative Licensing Law that forbids exclusion of non-local products and services. Both passengers and drivers should be given the equal access to enjoy the dividends of the sharing economy, which has greater potentials to optimize urbanization and improve employment than overreaching governance.
The author is deputy director of the Communication Law Center at China University of Political Science and Law.