Using needles to help life's energy flow


Solid studies
Through studies conducted over the last century, scholars now have a relatively deep understanding of the working mechanisms of acupuncture, says Jing Xianghong, director of the Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion at the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences.
Chinese scientists have accumulated a great deal of information in the study of acupuncture analgesia, the sensitization of acupoints, and the effects of acupoint stimulation, she adds.
In TCM, acupoints reflect the body's internal condition. When diseased or injured, corresponding acupoints become sensitized, displaying effects like expanded receptive fields, heightened pain perception, and increased heat sensitivity, which gradually disappear as the body heals.

In 2021, Ma Qiufu, a professor at Harvard University, co-authored a paper, titled A Neuroanatomical Basis for Electroacupuncture to Drive the Vagal-Adrenal Axis, with researchers from China including Jing, which was published in the journal Nature.
Since then, basic scientific research on acupuncture and moxibustion has once again drawn the attention of researchers, Jing says.
She adds that, based on existing studies, it is possible to conclude that the transmission and integration of the nervous system are essential for acupuncture to work. The neuroendocrine-immune network serves as the primary carrier for acupuncture's modulating effects, and molecular biology provides the material basis for explaining the effects of acupuncture.
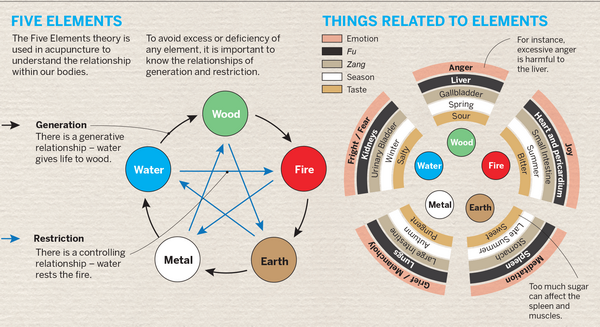
In simpler words, the studies show that the nervous system plays a crucial role in acupuncture. It relies on a network that involves the nervous system, hormones, and the immune system. Molecular biology also helps explain how acupuncture works.
Last year, professor Xu Nenggui and a research team from the Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine published Evidence Mapping and Overview of Systematic Reviews of the Effects of Acupuncture Therapies in the British Medical Journal.
The study established the most comprehensive database and data matrix for acupuncture clinical effectiveness research to date, and recalculated the effect values of acupuncture for each disease. The paper suggests which diseases and conditions acupuncture can substantially benefit and which show promise but still require further study, says Lu Liming, who was part of the team.
Xu says the study can help acupuncturists and researchers make decisions quickly in clinical practice and research.
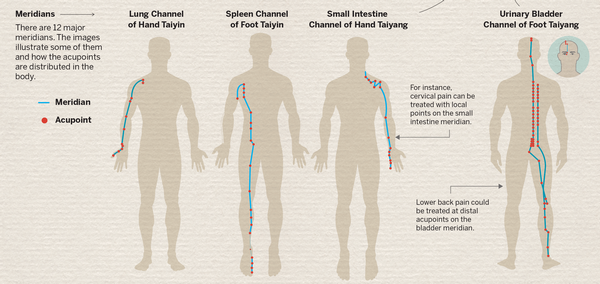
Liu says acupuncture's advantages lie in the fact that it is an external technique, so it is safer than taking medicine, and is effective in treating many conditions.
According to the study by Xu and his colleagues, acupuncture can substantially benefit post-stroke aphasia, neck and shoulder pain, fibromyalgia, nonspecific lower back pain, vascular dementia, postpartum lactation insufficiency and allergic rhinitis.
Yang is working on the research into the therapeutic effect of acupuncture for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, a common inner ear condition causing sudden and intense dizziness triggered by movements of the head. The condition is caused by small ear crystals that have become dislodged. He found that after the treatment commonly used to reposition the crystals, five rounds of acupuncture can effectively reduce remaining dizziness, as well as relieve anxiety about any sudden reoccurrence.
In addition, based on strict randomized controlled trials conducted by researchers around the world, acupuncture has been found effective in treating conditions such as chronic severe functional constipation, female stress urinary incontinence, and migraine, Jing says.