Silver is the new gold in China's economic mosaic
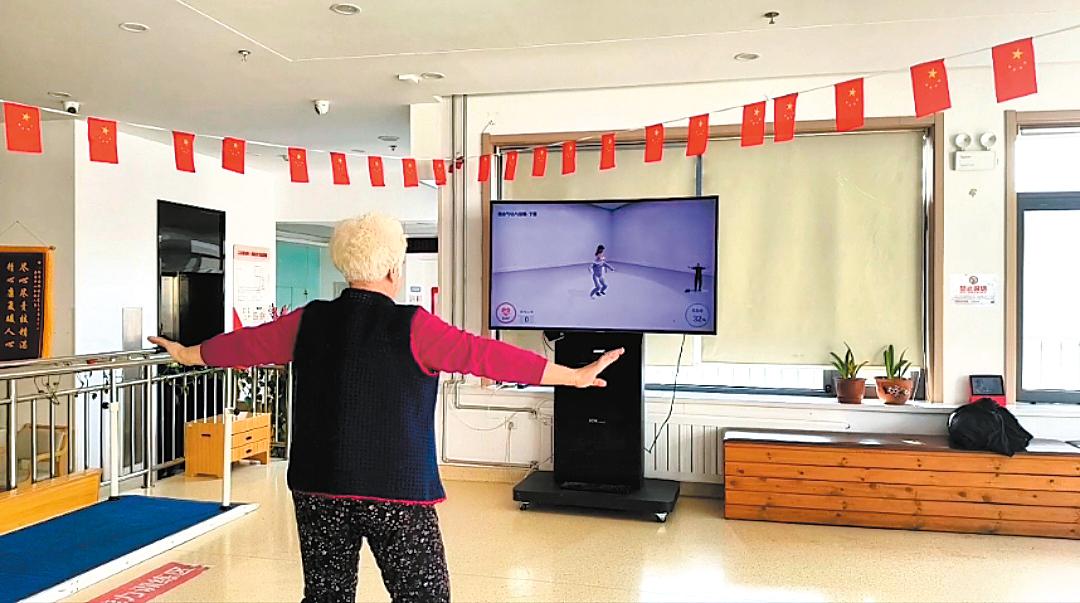


Following the instructions on a screen, an elderly lady exercises at the Yuexiu Road Elderly Care Service Center in Tianjin. CHINA DAILY
Chinese modernization is intertwined with reform and innovation. China's rapidly rising ageing population, alongside its technological and industrial advancement, is opening up a new economic frontier: the "silver economy". From just a peripheral concept, the silver economy is emerging as a promising area for growth, reform, and innovation.
Described not only as economic activity that serves senior citizens but also as a broader preparation for an ageing society, the silver economy is a cross-sector economy dedicated to elderly people in our societies and impacts industries and markets across the economy.
According to the National Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2024, the number of Chinese people aged 60 or above was 310 million, accounting for about 22 percent of China's total population. This means China is now a moderately ageing society. By 2035, the UN's World Population Prospects 2024 projects the figure will exceed 400 million, crossing the 30 percent threshold to turn China into a severely ageing society. And by 2050, about 500 million people — or nearly 40 percent of the population — will be 60 or above, making China a "super-aged" society.
Add to that the broader silver demographic — those aged 50 or above — and the numbers become even more striking: 530 million in 2024, more than 600 million by 2035, and nearly 680 million by 2050. By the 2040s, more than half of China's population will be "silver", making them the primary consumers, and transforming the country's socioeconomic landscape.
Globally, China is expected to remain the country with the largest elderly population through the middle of the 21st century.
Since, on average, one in every four elderly person in the world lives in China, the demographic foundation for developing a robust silver economy is not only strong but also unparalleled.
The consumption power of China's "silver generation" is being re-evaluated. Unlike their predecessors, the post-1960s cohorts — the first to benefit from China's reform and opening-up — have already retired or are moving toward retirement but with higher income levels, better education, and a broader outlook.
Their peak earning years coincided with a period of rapid income growth: from double-digit monthly incomes in the 1980s to five-digit incomes in recent years. According to the 2020 national census, 7.5 percent of the post-1960s, 15 percent of the post-1970s, and more than 30 percent of the post-1980s generations received higher education. With higher incomes and greater willingness to spend, the "new silver consumers" are shifting from survival-based to lifestyle-oriented consumption.
Their spending extends beyond products like food and housing to quality healthcare, travel, smart homes, digital tools, cultural products and personalized services. In this transition, quality, diversity, personalization and convenience are the new benchmarks, and they are transforming the elderly people into increasingly important contributor to economic activity.
The convergence of an ageing society and the digital age has generated a powerful momentum. Emerging technologies — from AI and 5G to big data, quantum computing, and digital healthcare — are being applied to meet the needs/demands of the elderly people.
This shift is fueling three key transformations. First, it is fueling the rise of new "silver industries". By integrating frontier technologies such as AI, smart materials, biomedicine, and green energy, China is developing sectors such as intelligent eldercare, smart manufacturing, age-friendly financing, and healthy living.
Second, it is helping create new products and services. From elderly friendly wearables and smart home systems to anti-ageing treatments, cultural tourism and digital companionship platforms, innovation is giving rise to a high-tech-driven and scalable industry with global potential.
And third, the shift is facilitating the cultivation of new market standards. High-quality eldercare services, including silver-focused education, nutrition, home services and tailored financing — are becoming more standardized and brand-driven, creating room for specialization and mass-market appeal.
China's silver economy is multi-dimensional and innovation-driven. Instead of being a knee-jerk reaction to the ageing population problem, it is a way to make full use of a strategic opportunity in the modernization process. Developing the silver economy is essential to building a modern economic system, upgrading the industrial structure, and improving the well-being of hundreds of millions of people.
The race to adapt to population ageing is on. With a proactive, tech-enabled, and people-centered approach, China is positioning itself to play a significant role in the global transformation toward silver-oriented development.
The author is a professor at the School of Economics, Nankai University. The views don't necessarily represent those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.