Chinese satellite reveals mysterious cosmic 'fireworks'

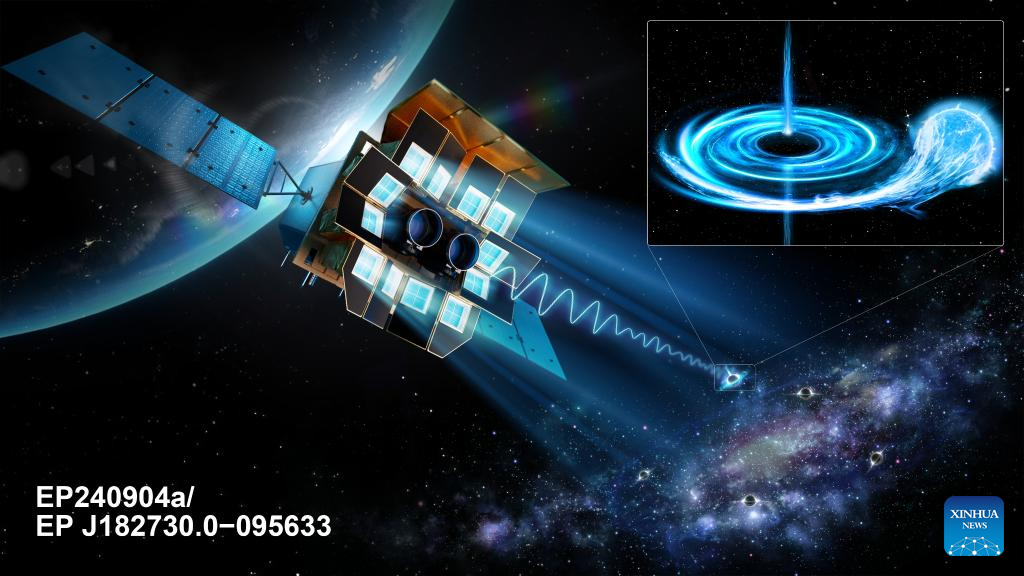
BEIJING -- In the course of almost two years after China's astronomical satellite named Einstein Probe was launched, it has managed to capture many extraordinary transient events in the universe that flicker like fireworks, thereby helping expand human understanding of extreme physical phenomena in the cosmos.
"Since its launch in January 2024, EP has fundamentally transformed our view of the dynamic X-ray universe. This pioneering mission, led by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, is now delivering a steady stream of discoveries — uncovering rare and explosive cosmic events that were once too brief and faint for other telescopes to catch," Yuan Weimin, principal investigator of the EP mission and a researcher at the National Astronomical Observatories of the CAS (NAOC), said recently.
The EP mission is one of a series of space science missions under the leadership of the CAS. It is also an international collaboration mission with contributions from the European Space Agency, the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany, and the French space agency CNES.
The probe is equipped with two complementary X-ray telescopes. Its Wide-field X-ray Telescope (WXT) utilizes novel lobster-eye optics to monitor one-tenth of the entire sky in a single shot, thus providing unprecedented sensitivity to faint, transient events. For detailed follow-up, the Follow-up X-ray Telescope (FXT) offers a larger effective area and superior angular resolution to pinpoint and study discoveries.
"The probe can capture fleeting flashes, monitor processes with a duration from seconds to days and years, and detect faint signals hidden in the dark. These findings establish EP as a key player at the forefront of international research in time-domain high-energy astrophysical observations," said Yuan.
SLOW EVOLVING COSMIC FIREWORK
EP discovered a new X-ray transient, EP241021a, persisting for at least 40 days, like a slowed-down cosmic firework, which was accompanied by a relativistic jet. Relevant study has been published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Such a prolonged and luminous eruption is extremely rare. Astronomers speculate it could be the signature of a star being torn apart by an uncommon intermediate-mass black hole or an unusual type of explosion resulting from the core-collapse of a massive star.
"This discovery offers new insights into catastrophic explosion and the launching of a relativistic jet," said Shu Xinwen, a professor at Anhui Normal University in east China, who leads the study.
"It also provides potentially valuable clues for studying the enigmatic class of intermediate-mass black holes," Shu added.
ILLUMINATING THE MILKY WAY
In September 2024, the probe captured an exceptionally faint X-ray burst, dubbed EP240904a, within the Milky Way. Its observational characteristics, including its X-ray "heartbeat" and spectral evolution, as well as its radio and infrared properties — identified it as a new black hole candidate. The outburst was about 100 times dimmer than typical black hole eruptions, explaining why it had remained hidden in previous observations. Relevant study has been published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
"The discovery of EP240904a opens a new window for unveiling the hidden population of black holes in the Milky Way," said Cheng Huaqing from the NAOC, who is the first author of the study.
"With the EP, we now have the key capability to uncover these 'silent' black holes systematically," said Tao Lian, a researcher from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the CAS and corresponding author of the study.
RARE X-RAY FLASH
The mission's autonomous capabilities were spotlighted with the discovery of EP240801a. The probe detected this transient and immediately triggered its onboard FXT instrument for follow-up observations.
A joint analysis involving NASA's Fermi satellite revealed the event to be an extremely "soft" X-ray flash — a rare type of explosion in which low-energy X-rays dominate radiation.
Scientists classify X-rays as "soft" or "hard" based on the energy level of their X-ray photons. Soft X-rays have lower photon energy, while hard X-rays have higher energy.
Its extreme properties provide new clues regarding the diversity of gamma-ray bursts and stellar core-collapse events.
"This event showcases EP's core capabilities — as it completed the full process from discovery to tracking the X-ray evolution and locating the position of the transient source autonomously," said Xu Dong, a researcher from the NAOC. "This performance marks it as a brilliant and efficient cosmic monitoring platform."
- Chinese satellite reveals mysterious cosmic 'fireworks'
- Xinjiang sees 26-fold surge in tourist tax refunds in first 10 months
- Shanghai East Hospital launches multidisciplinary thoracic care model
- Intl experts, new tech guide Shanghai's green fuel ambitions
- Hunan shop owner's accusations against officials, herbicide video sparks investigation
- China hits record 180 billion parcel deliveries





































