Xinjiang finds new medical approaches
 |
|
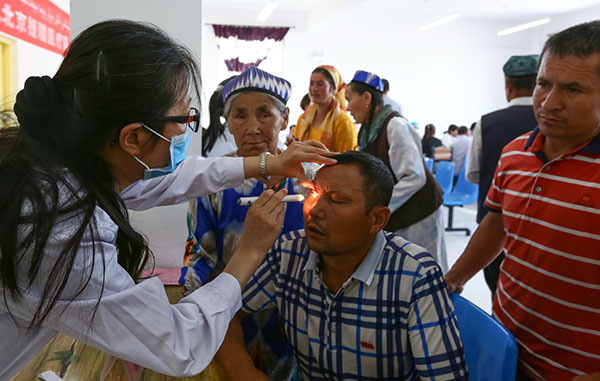
Liu Weihua, an eye doctor from Beijing Tongren Hospital, checks a resident of Hotan, in the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, earlier this month.[Xu Zhuzhu/For China Daily] |
Support from outside giving way to better training within the region itself
Patients diagnosed in the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region with a dangerous type of gallstone once had to travel to the capital, Urumqi, or even to another province, for treatment because of a shortage of specialists.
The costs involved meant that many sufferers simply soldiered on with a condition that, if left untreated, could result in a deadly infection.
Yet that all changed in 2015 when Uygur surgeon Memeturson Barat returned from a yearlong training program in Guangzhou, Guangdong province, which was organized as part of a central government effort to cultivate medical resources in Xinjiang.
"When medical treatment is available on your doorstep, it saves people so much trouble and tons of money," said Barat, 32, who now specializes in digestive medicine at No 1 People's Hospital in the border city of Kashgar.
A number of patients in the northwestern region with serious conditions have seen similar changes in recent years, according to Wang Junhua, deputy director of the training center at Xinjiang Women and Children's Hospital.
"In remote parts of the region, the mortality rate for women during childbirth is higher than in cities because of the lack of medical staff and expertise. Most of the deaths are preventable," she said.
People can get surgeries like esophageal foreign body extraction and EMR (a procedure to remove polyps in the digestive tract) from local doctors in Kashgar after more emphasis was placed on coaching local medical professionals through the Xinjiang health assistance program.
According to the National Health and Family Planning Commission, more than 10,000 professionals have received training through the program, which has paired hospitals in the region with those in major cities since 2012.
Over the period, some 3,300 medical trainers from other provinces have been sent to Xinjiang, and around 590 local professionals have studied outside the region.
The medical assistance program for Xinjiang kicked off more than two decades ago. Nearly 50,000 medical experts from around China have been sent to the region, but the lack of capable doctors and medical expertise is still one of the factors holding back Xinjiang's health and medical progress, because when the experts leave conditions slide back to their original levels.
In 2011, the central government brought a new assistance program to Xinjiang. It requires 19 provinces, municipalities and ministries to support Xinjiang's development in different fields. In the health sector, more emphasis has been put on cultivating a medical corps that will stay long-term.
For instance, Jiangsu province paired one of its medical experts with three Xinjiang doctors and incorporated their performance into their annual assessments. Fujian province has sent 100 medical experts to Xinjiang every year, and it receives 100 doctors from the region to study and work in Fujian, according to the Xinjiang Health and Family Planning Commission.
In addition to training opportunities, Xinjiang has also crafted preferential policies to boost the development of local medical professionals, including making it easier for local doctors to earn qualifications and get promotions, and exempting medical students from tuition fees if they serve in certain places in Xinjiang, according to the national health commission.
"We have been innovating the talent training mechanism - changing from getting blood transfusions to forming blood on our own," Yin Yulin, deputy director of the Xinjiang commission, said of the new effort at a work conference on July 13.
Li Xinwei, head of the South Xinjiang workstation of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, said: "We have been talking about assistance for Xinjiang for many years, but I prefer the concept of building up Xinjiang. We should put more emphasis on training our own medical professionals and standing on our own."
Li Lei contributed to this story.























